Are your AI videos blurry and weird? Most tools ignore 500-word prompts. These 7 styles stay short, repeatable, and actually work across platforms.. Ai Tools, Prompt Engineering, Ai Fire 101, 🔥 Ai Fire Academy.
TL;DR BOX
Mastering 7 specific prompt styles enables creators to generate professional videos using any AI video tool without complex descriptions. These frameworks provide directorial control over camera movement, pacing and consistency across all major AI models.
Users often fail with overly complex prompts that AI ignores. Techniques like “Timestamp Prompts” enable precise planning by defining actions second by second, transforming chaotic generation into controlled editing. To solve visual inconsistency, “Image Prompts” and “Anchor Prompts” are essential, referencing base images or specific physical details to ensure characters and styles remain uniform throughout a sequence.
Key points
-
Stat: Timestamp prompts divide videos into exact segments (e.g., 0-3s), forcing the AI video tool to follow to a strict timeline.
-
Mistake: Relying on text alone for consistency; use Image-to-Video to “lock in” the visual style effectively.
-
Action: Use “Cutscene Prompts” to merge multiple camera angles, like a wide shot and close-up, into one generation.
Critical insight
“Anchor Prompts” act as insurance against AI hallucinations, forcing the model to retain specific physical details like scars or props across different scenes.
Table of Contents
I. Introduction: Why Your Prompts Are Failing
Have you ever wasted hours writing ‘perfect’ AI video prompts… and the videos still came out messy. Blurry motion. Weird physics. Characters changing for no reason.
Now we found the truth: AI video tools don’t reward longer prompts. They reward director-style structure.
So I broke it down into 7 prompt styles. These aren’t random tips. These are the foundational frameworks that work across every AI video tool: Veo, Sora, Kling, Runway, Pika – most tools respond to these the same way.
Master these seven and you’ll stop guessing. You’ll know what to do when a video comes out wrong.
II. Prompt Style #1: Cinematic Prompts – Control the Camera, Control the Emotion
Cinematic prompts focus on how the camera moves and observes the scene, not just what is in the scene. The same subject can feel completely different depending on camera movement.
Dang, it sounds like we’re movie directors. And yes, yes we are. Let me introduce you to two of the easiest shots you can apply right now in your AI video tool.
Example: The Artist in the Studio
Like usual, I bet we would say “an artist in the studio”. Bruh, that is boring and makes you look like an amateur. Let’s fix it with these prompts:
-
Static Shot: “A static shot of an artist standing alone in a dimly lit studio. The camera remains perfectly still”. (Result: Calm, contemplative, isolated).
-
Rotating Zoom-In: “A slow circular dolly around the artist while the camera gently zooms in. Soft handheld drift. Dim studio lighting”. (Result: Intimate, emotional, internal).

Camera Movements That Change Everything
Interested, right? Go with me to another level with these other camera movements to make your video more dynamic:
-
Tracking Shot: Moves alongside the subject (creates flow and movement).
-
Handheld Drift: Subtle instability (adds realism and human tension).
-
Overhead Shot: Top-down perspective (creates distance or observation).
-
Circular Dolly: Moves around the subject (reveals creative space and context).
-
Vertical Tilt: Tilting upward suggests hope or inspiration; tilting downward suggests tiredness.
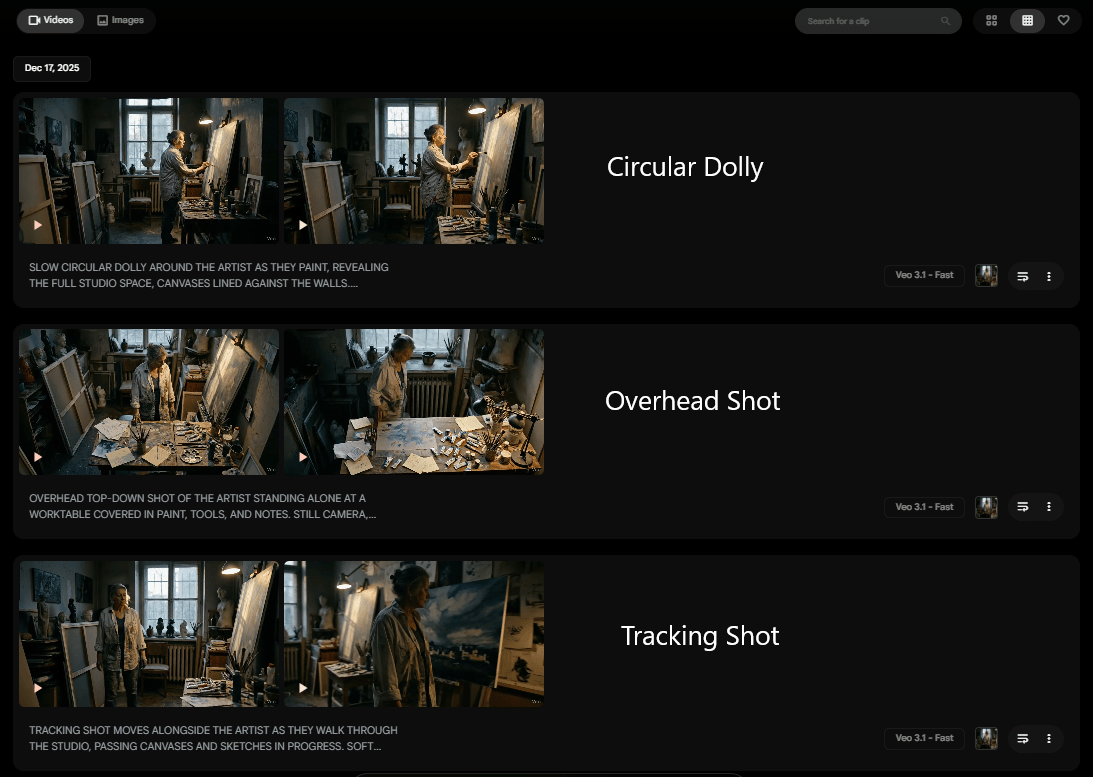
Once you know the camera move you want, here’s my pro tip: combine two moves.
Here is an example of this kind of prompt: “The camera begins with a slow tracking shot behind the artist, tilts up to their face, then circles around to reveal unfinished canvases surrounding them”. I generated one cinematic video but it has two sequences in a single shot.

Combine Movement Video.
My key insight: Cinematic prompts give you directorial control. You aren’t just generating video; you are choosing how the audience experiences the scene through the AI video tool.
Learn How to Make AI Work For You!
Transform your AI skills with the AI Fire Academy Premium Plan – FREE for 14 days! Gain instant access to 500+ AI workflows, advanced tutorials, exclusive case studies and unbeatable discounts. No risks, cancel anytime.
Start Your Free Trial Today >>
III. Prompt Style #2: Timestamp Prompts – Divide Your Video Into Controlled Segments
Sometimes you want multiple things to happen in sequence. If you throw it all into one prompt, the AI video tool often messes up the timing.
Want to fix that? Open your notebook and write this prompt down. This is my secret weapon for control. Instead of hoping the AI figures out the pacing, you tell it exactly when to do things. You can divide your video into seconds.
Example: The Night-Shift Barista (8-Second Video)
Take this as your first lesson. Instead of saying “this thing happens first, this thing happens next,…” bla bla bla. Why don’t we guide it by the second it should happen, like this:
-
0-3 seconds: “The camera slowly pans across a quiet coffee shop at night, stopping on a barista behind the counter”.
-
3-5 seconds: “The camera pushes in as the barista pours steaming milk into a cup, focused and precise”.
-
5-8 seconds: “The camera tilts up to the barista’s face as they pause, exhale and look out the rain-streaked window”.
Result: The AI video tool follows the sequence way more often, because you gave it a timeline, instead of chaotic randomness. This turns you from a gambler into an editor. You are dictating the timeline.
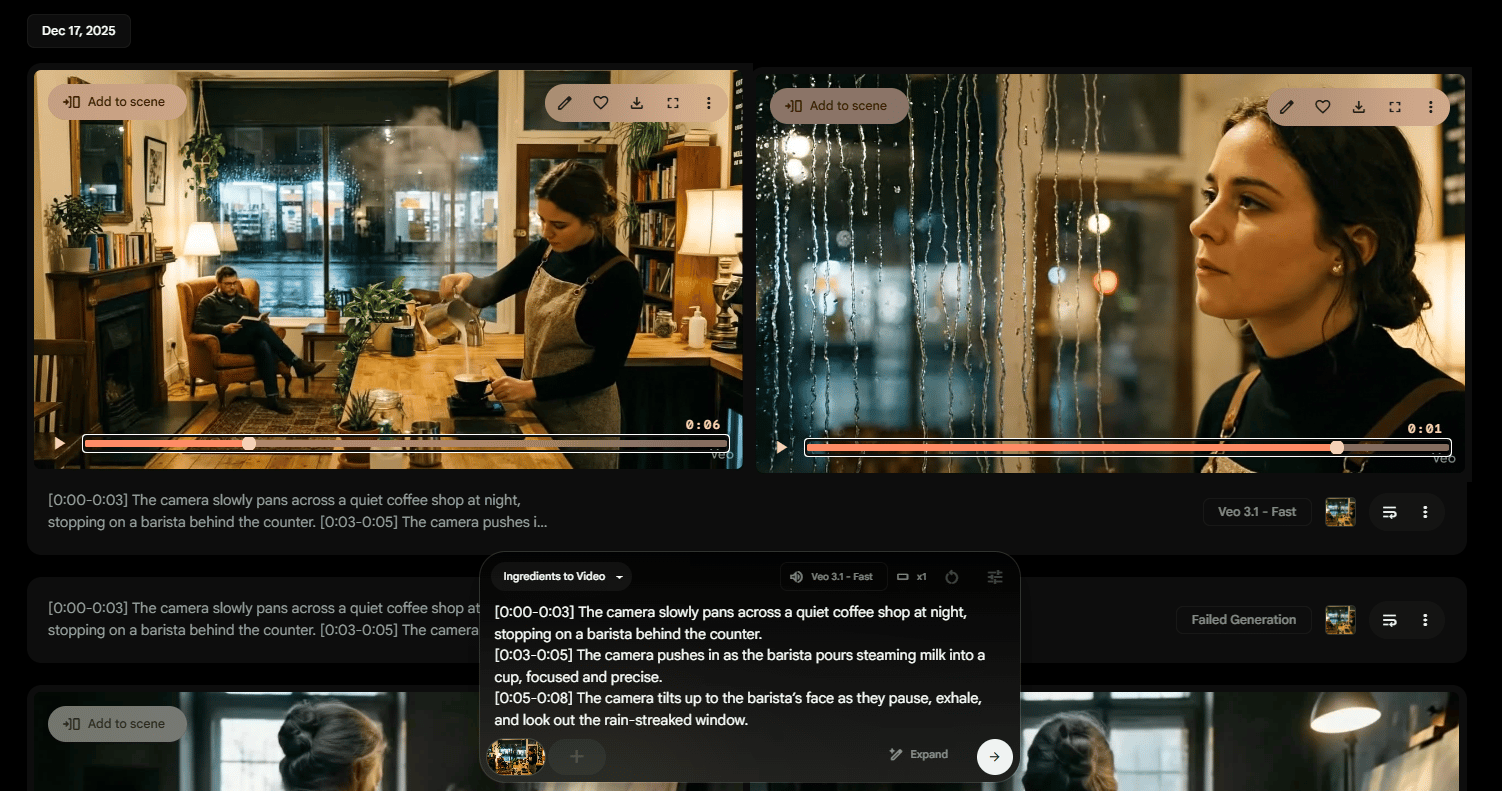
The left is the first scene and the right is the last scene.
When you should use this prompt: You need multiple camera movements, precise timing or a mini-story arc (setup → action → resolution).
Timestamp prompts turn AI into a storyboard tool. You are planning the scene frame by frame.
IV. Prompt Style #3: Cutscene Prompts – Multiple Camera Angles in One Video
Want to look like a pro editor without opening Premiere Pro? Let me help you script “cuts” directly into your prompt.
Timestamp prompts control when things happen. Cutscene prompts let you change camera angles entirely within a single video generated by your AI video tool, like editing in post-production but during generation.
Example: The Street Photographer
Here is the prompt I used:
“The photographer walks slowly through a city alley, camera hanging from their neck. Cut to a close-up shot of their fingers adjusting the lens and pressing the shutter inside a cinematic film”.
Result:
-
First Half: Wide, full-body shot of the photographer walking through the alley.
-
Second Half: Close-up shot of hands adjusting the camera lens and clicking the shutter.
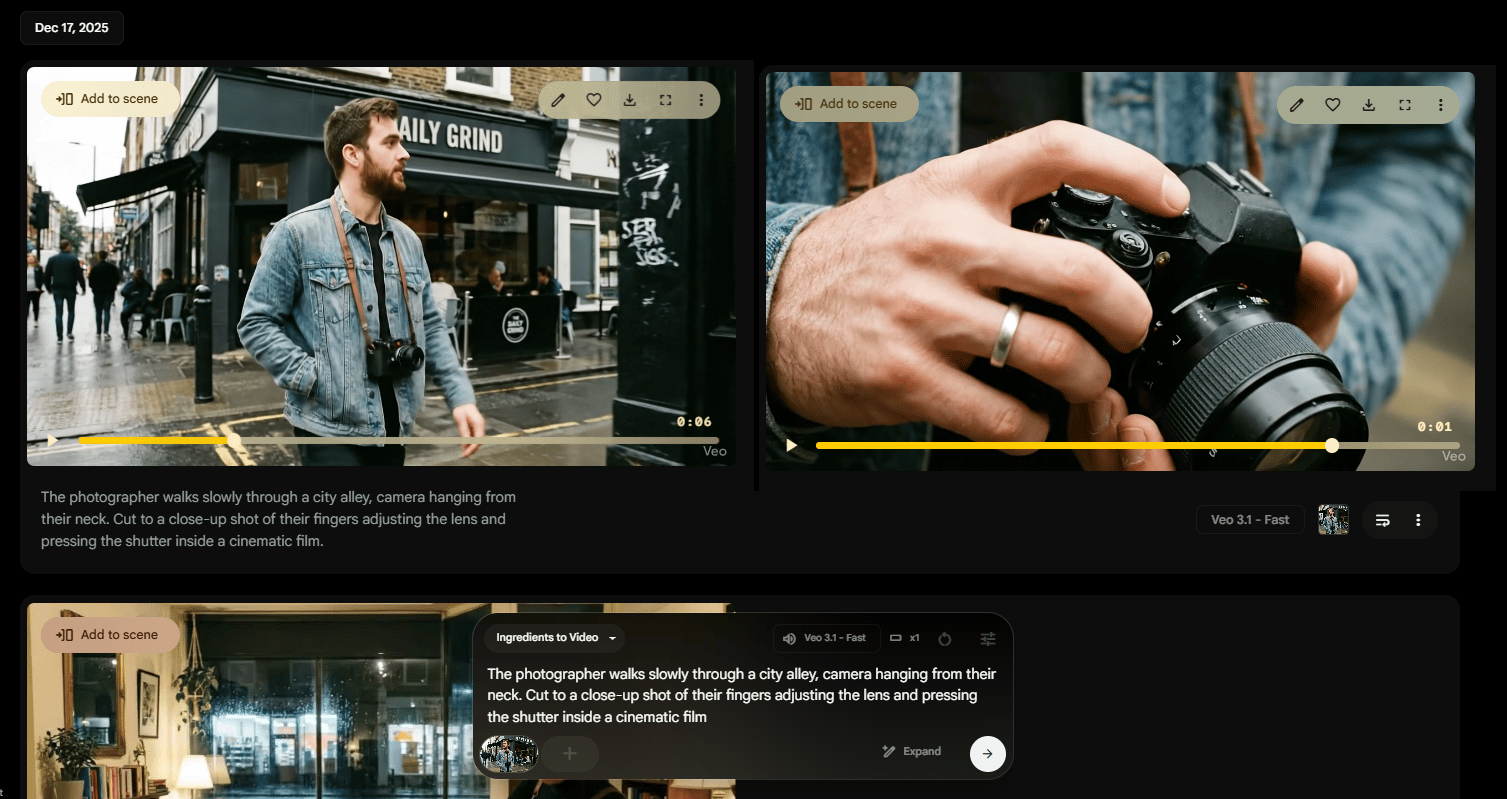
The left image is the first half and the right one is the second half.
It’s good BUT let me show you something even better. Remember the previous lesson above, the Timestamp prompt. Why don’t we combine these prompts into one? Let me introduce you to the “Timestamp + Cutscene”:
-
0-3s: “Wide shot of a photographer walking through a narrow city street at dusk”.
-
3-5s: “Cut to a close-up shot of their eye looking through the camera viewfinder”.
-
5-8s: “Cut back to a medium shot as they stop and take a photo”.

My 8-second video with the combining prompt.
Warning: I know this prompt is great but we need to know our limits. If you cut to something totally different (like a 3D animated scene inside a realistic movie), the AI video tool might freak out and lose the style. Keep the scenes visually similar to stay safe.
My key insight: Cutscene prompts turn you into an AI director, managing multi-angle storytelling within a single generation.
V. Prompt Style #4: GPT Prompts – When Should AI Write Prompts for You?
Cutscene prompts let you change camera angles inside one generation by writing “cut to…” directly in the prompt. It’s like doing basic editing during generation. The trick is keeping the style consistent so the model doesn’t break.
Key takeaways:
-
Use “cut to close-up”/“cut back to medium shot.”
-
Keep environments and style similar across cuts.
-
Combine with timestamps for maximum control.
-
Don’t jump between totally different art styles.
Cutscene prompts let you create multi-angle storytelling without opening an editor.
We’re so close to 2026, so why don’t we apply the term “Work smarter, not harder”? Why write prompts yourself when you can train an AI to do it for you? If you are already using AI to generate videos, use AI to generate the prompts themselves.
There are many ways to do this but I’ll use the Custom GPTs feature on ChatGPT as an example.
The Right Way to Use GPT Prompts
I use GPT for one job only: structuring prompts, not inventing complexity. My rule is simple:
-
Find the official prompt documentation for your tool (e.g., Google Veo 3.1, Sora 2).
-
Create a custom GPT in ChatGPT.
-
Upload the documentation as knowledge (PDF, Doc, even plain text if you can).
-
Job Description: “You are a prompt helper for Google Veo 3. I give you a scene, you generate an optimized prompt”.


GPT Prompts Example
To be honest, this method has a deadly problem that GPT doesn’t know the AI video limitations. So, mainly it will generate videos with some weird action.
Okay, let me take an example, when I want a prompt to generate a video about the angry crowd pointing at my protagonist, it might write: “The crowd of angry townspeople surrounds her”.
Cinematography: Wide shot. Handheld camera with slight shake to capture chaos in a medieval village square.
Scene: A tall elven woman in black leather armor sits on a chestnut horse at the center of the crowd. Townsfolk shout angrily and throw debris - stones, vegetables, torn cloth - while guards try to restrain them. The mob presses closer.
Character Emotion: The elf’s expression shifts from defiance to fear as control slips away.
Sound Design: Echoing shouts. The horse neighs in panic. Boots scrape against cobblestone.
Ambient Audio: Wooden shutters slam. A distant church bell tolls.
Lighting: Late afternoon. Overcast skies. Muted warm tones mixed with smoke and dust.
Mood: Tension. Danger. Loss of control.
Style & Atmosphere: Gritty medieval fantasy. Cinematic realism. Dynamic camera motion. Shallow depth of field focused on the elf and her horse, with the background slightly blurred. The air is smoky, filled with flying embers and swirling dust, creating a sense of chaos and rebellionWhen I tried this in Veo, it looked REALLY AI because crowds are still a weak spot.

To fix this, you must keep the same emotion but make it easier for the AI to render, like this:
Medium tracking shot. A female elf rides slowly on horseback through a quiet medieval village street, her eyes scan the crowd with growing unease. The townsfolk watch in silence, too still, too calm. The horse snorts and shifts, nervously as distant church bells toll, faint and hollow.
SFX: muffled footsteps, leather creaking, a low ambient hum of tension.
Style: dark fantasy realism, muted daylight, slow camera movement, subtle wind stirs cloaks and dust, ominous mood.
My key insight: GPT is great at language. AI video tools are bad at complex scenes. So let GPT write the structure, then you remove anything that pushes the model past its limits. That’s how you get clean, cinematic results instead of blurry, overcooked chaos.
VI. Prompt Style #5: Anchor Prompts – Remind the AI What Matters
Have you ever been like me? I mean, when you want the AI to generate a video about a man with a scar on his face (for example) but the result is horrible. The protagonist’s face suddenly becomes normal, like the scar isn’t even there, even though my protagonist doesn’t have healing powers.
AI does weird stuff, right? Things that seem obvious to you are not obvious to the AI.
Example: The Exhausted Chef
This example will help you fix that problem, so you don’t have to worry about making a movie; your main character will not look like Brad Pitt in one scene and Danny DeVito in the next.
-
My Prompt:
The chef is happy, joyful, laughing and has a wide smile.-
The AI: I thought my chef would be smiling, remove sweat and make the kitchen spotless. But it turned out even worse. My chef doesn’t smile, laugh or look happy.

-
The Anchor Fix:
The chef is happy, joyful expression as his eyes grow blue and the long scar. He keeps a wide smile while serving the customer.
When to Use Anchors:
-
Physical Appearance: Ensuring scars, wrinkles, dirt, age or wear don’t disappear.
-
Positioning: This one is hard to explain so I’ll use this prompt as an example:
-
Anchor off: “The orc warrior rides a dark wolf and charges straight at the soldier. In one brutal motion, he cuts the soldier down with his massive blade, muted colors, gritty, cinematic medieval tone”. The result I get is the orc sliding off the wolf during the fight, which is weird and makes no sense.
-
So let’s turn on the anchor by adding this detail in the prompt: “The orc is on the back of the direwolf, riding it.” Now the result is what I expected.

-
Off-Screen Details: This anchor prompt helps the AI keep scene details consistent later on that it can’t see right now. Let me give you a quick example: you want a warrior who only has armor on the left shoulder. So, to maintain this detail, you need to use this anchor prompt to keep this detail in all scenes of the video. Simple, right?
My key insight: Anchors are your insurance policy against AI assumptions.
VII. Prompt Style #6: Image Prompts – The Secret to Consistency
Text helps. But if you want real consistency, you and I both know the cheat code is Image-to-Video.
To get the most beautiful, consistent shots, we need to use image prompts. Text alone cannot consistently produce specific visual styles or consistent characters.
The Workflow:
Right now, the Image-to-Video feature is common in most of the AI-generated video platforms but the workflow is similar. Let me show you an example:
-
Generate an Image (Midjourney/Nano Banana Pro): “Hyper-detailed cyberpunk illustration of a street photographer standing under neon lights in Tokyo at night”.
-
Animate It (Kling/Runway): “The photographer slowly raises the camera and steps forward through the rain”.

Result: The image establishes the style and composition. The text prompt just describes the motion.
Consistent Characters Across Shots
This is basically a “frame-to-video” method but stronger. Here is my workflow for this trick:
-
Generate a base image of your character.
-
Use AI (like Nano Banana Pro) to generate variations: side profile, sitting, walking.
-
Animate each image separately. Now you have multiple consistent shots of the same character performing different actions.
Want to make it stronger? Even if you say yes or no, I have to tell you about this tool. Because it’s awesome and I don’t want to keep it alone, you could assume this as my bonus tip.
I just found a cool tool in Hugging Face called “Qwen Image Edit (Camera Angle Control)”. This gives you total control. You aren’t hoping the AI makes him jump correctly; you are forcing it to connect the dots between point A and point B. All I need to do is upload the image and adjust the angle.

My key insight: Image prompts are the foundation of professional AI video. Text describes motion; images define style.
VIII. Prompt Style #7: Negative Prompts – Tell the AI What NOT to Do
This one is actually the easiest thing you can learn immediately. Sometimes it is easier to tell the AI video tool what you don’t want. I make it clearer with these examples below.
Example: The Futuristic City Skyline
My problem with the video is that the AI keeps adding flying cars that clutter the scene. And I don’t like that; I didn’t even mention “flying vehicles” or “drones”. I just used the Negative Prompt.
To use this, you just type what you hate, like “No flying vehicles. No drones. No traffic in the sky”. It usually removes them. If it doesn’t, repeat the negative prompt and simplify the rest.

Example: The Meditating Monk
My second example is about removing sound. So, I don’t like the way AI adds dramatic chanting or background music. My negative prompt fix may look like this: “Total silence. No chanting. No music. No ambient sound”.
The result is a video that is completely silent. Now I can add any ambient sounds into the video from my own library.

My key insight: Negative prompts are precise corrections. You should use them when the AI’s default assumptions conflict with your vision.
IX. How Do You Combine All 7 Prompt Styles?
You don’t use all seven every time. You pick the ones that solve the problem in front of you. A simple build order works best: lock style first, then control time and angles, then clean up errors.
Key takeaways:
-
Start with Image prompt to set style.
-
Add Cinematic movement to set mood.
-
Use Anchors to lock key details.
-
Use Timestamps + Cutscenes for sequencing and angles.
-
Use Negative prompts to remove distractions.
-
Use GPT only to draft, then simplify.
When you combine them, you stop hoping the model “gets it.” You start directing.
Once you understand the seven prompt styles, everything starts to click. You stop guessing and start building scenes on purpose.
This is how I combine them to create a simple 30-second short film. Each shot uses a different prompt style but they all work together as one flow.
-
Shot 1 (0–8s): I start with a strong image prompt to set the scene, then guide the camera slowly toward the character’s face. I anchor key details, like ash on the armor and block anything distracting, like music.
-
Shot 2 (8–16s): Here, I control timing. I tell the AI exactly what happens in each half of the shot, using cuts and close-ups to add emotion.
-
Shot 3 (16–24s): This is where I lean into cinematic movement. I let the camera orbit the character while removing anything unnecessary from the frame.
-
Shot 4 (24–30s): I finish with a clear end frame. One strong action, handheld motion and no extra instructions to confuse the model.
When you use these styles together, you’re no longer hoping the AI “gets it.” You’re directing the scene.
X. 1-Screen Cheat Sheet: Which Prompt Style Fixes Which Problem
|
Your Problem |
Use This Prompt Style |
What It Fixes |
|---|---|---|
|
Video feels flat or boring |
Cinematic Prompt |
Controls camera movement, mood and emotional impact |
|
Timing is messy or rushed |
Timestamp Prompt |
Forces clean pacing and exact sequencing |
|
You want multiple angles in one video |
Cutscene Prompt |
Creates professional camera cuts inside one generation |
|
Prompts take too long to write |
GPT Prompt (Draft Only) |
Speeds up structure, not decision-making |
|
Character details keep changing |
Anchor Prompt |
Locks scars, clothing, props, positions |
|
Style changes between shots |
Image Prompt |
Freezes visual style and character consistency |
|
AI adds things you didn’t ask for |
Negative Prompt |
Removes unwanted objects, sounds or behaviors |
My rule is simple:
-
Style breaks? → Image + Anchor.
-
Timing breaks? → Timestamp.
-
Emotion breaks? → Cinematic.
-
Logic breaks? → Simplify (don’t add more words).
You don’t stack all seven every time. You apply the one that fixes the problem in front of you. Use the cheat sheet above to decide which styles to combine.
XI. Conclusion: From Beginner to AI Director
The difference between someone who “uses AI video” and someone who masters AI video is understanding that prompting is a craft, not a guessing game.
These seven prompt styles aren’t random tricks – they’re the basic techniques that AI filmmakers use every day.
-
Cinematic = Control the camera.
-
Timestamp = Plan sequences.
-
Cutscene = Visual variety.
-
GPT = Speed up writing.
-
Anchor = Keep details.
-
Image = Establish style/consistency.
-
Negative = Remove distractions.
Master these seven and you will never struggle with AI video generation again. The future of filmmaking isn’t about who has the best equipment; it’s about who understands how to direct AI.
And now, you do.
If you are interested in other topics and how AI is transforming different aspects of our lives or even in making money using AI with more detailed, step-by-step guidance, you can find our other articles here:
-
21 Practical ChatGPT Hacks Real AI Masters Use to Work 2x Faster (Most Free)
-
Gemini 3 Pro UI Hack: The 4-Step System That Beats Hiring Designers
-
Is The New GPT-5 Good For Trading? The Brutal, Honest Answer*
*indicates a premium content, if any


Leave a Reply